LEOPARD syndrome is an autosomal dominant condition related to Noonan syndrome, although it occurs less frequently. The aim of this study was to characterize the clinical and molecular features of a large series of LEOPARD syndrome patients.
MethodsWe collected clinical data from 19 patients in 10 hospitals. Bidirectional sequencing analysis of PTPN11, RAF1, and BRAF focused on exons carrying recurrent mutations.
ResultsAfter facial dysmorphism, structural heart defects (88%) were the most common feature described. Hypertrophic cardiomyopathy (71%) was diagnosed more often than pulmonary valve stenosis (35%). Multiple lentigines or café au lait spots were found in 84% of the series, and deafness was diagnosed in 3 patients. Mutations in PTPN11 were identified in 16 (84%) patients (10 patients had the recurrent LEOPARD syndrome mutation, p.Thr468Met) (NP_002825.3T468M). Two other patients had a mutation in RAF, and 1 patient had a mutation in BRAF. When compared with other neurocardiofaciocutaneous syndromes, LEOPARD syndrome patients showed a higher prevalence of hypertrophic cardiomyopathy and cutaneous abnormalities, and a lower prevalence of pulmonary valve stenosis and short stature.
ConclusionsLEOPARD syndrome patients display distinctive features apart from multiple lentigines, such as a higher prevalence of hypertrophic cardiomyopathy and lower prevalence of short stature. Given its clinical implications, active search for hypertrophic cardiomyopathy is warranted in Noonan syndrome spectrum patients, especially in LEOPARD syndrome patients.
Keywords
.
INTRODUCTIONLEOPARD syndrome (LS), or Noonan syndrome (NS) with multiple lentigines (OMIM 151100), is an autosomal dominant disorder characterized by multiple lentigines or café au lait spots, electrocardiographic abnormalities, ocular hypertelorism, pulmonary valve stenosis or hypertrophic cardiomyopathy, genital abnormalities, constitutional growth delay, and deafness.1 LS shares many features with NS (OMIM 163950), which is characterized by an association with congenital heart disease, short stature, and craniofacial malformations2 but does not usually include multiple lentigines and deafness among its manifestations. Mutations have been identified in the PTPN11 gene in 50% of NS3–5 cases and in 85% of LS cases.6,7 Mutations in the RAF18 and BRAF9 genes have also been identified in LS. Although there are no exact data on its prevalence, it is thought that NS is present in 1 in 1000 to 2500 live births, suggesting that it is an underdiagnosed disorder.10 LS is less frequent, although precise data on its prevalence at birth are also unavailable. To date, at least 200 cases have been reported in the literature and a comprehensive review of the disorder has been published recently.11 Both disorders show considerable phenotypic variability, making them difficult to identify and diagnose correctly. Genetic studies can therefore provide a useful contribution to differential diagnosis. Diagnosis is also made difficult by the evolving and changeable nature of many of the condition's features. For that reason, any objectifiable congenital heart disease can provide valuable help in identifying the syndrome. We present a phenotypic description of a series of patients with LS characterized in genetic studies of the PTPN11, RAF1, and BRAF genes, and compare them with a large series of patients with other neurocardiofaciocutaneous syndromes (NCFCS) who were also characterized by the genetic study of mutations in the PTPN11, SOS1, RAF1, BRAF, and HRAS genes.
METHODSClinical EvaluationPatients were evaluated by clinical geneticists and pediatric cardiologists or endocrinologists involved in a Spanish multicenter study of genotype-phenotype relationships, and were diagnosed with LS using the criteria described by Voron et al.12 Blood samples or patient DNA were sent to our center from participating hospitals by the attending clinicians, who had previously obtained informed consent from patients. An initial clinical evaluation based on the preanalytical questionnaire described by Ezquieta et al.13 was used for case selection. Data on clinical characteristics relating to congenital heart conditions, skin changes, weight-to-height ratio, hearing problems, genital abnormalities, and patient facial characteristics were collected and stored in an Access database whose structure had been agreed among the clinicians involved. Facial phenotype was classified as typical when three or more of the following malformations were present: ocular hypertelorism, ptosis, low-set ears, and downward inclination of the palpebral fissures, and as suggestive when this criterion was not met. Height was assessed in standard deviations from a reference population14 and was considered low at<−2 standard deviations. All patients underwent electrocardiography and echocardiography evaluated by a pediatric cardiologist. Pulmonary valve stenosis was diagnosed using classic ultrasound criteria. Hypertrophic cardiomyopathy was diagnosed when the thickness of the left ventricular anterior wall was>2 standard deviations by age.
In 2 patients diagnosed with NS in which the genetic study identified a typical LEOPARD mutation, the patients’ evolution was monitored. The appearance of multiple lentigines was later confirmed, leading to a modification of the diagnosis (cases 1 and 8). With regard to the familial cases, a family of 3 members was evaluated clinically from the outset (family A), and subsequent genetic study confirmed the initial suspicion. In the other familial case evaluated (family B), the molecular study identified the mother of the index case as the mutation carrier, which led to further clinical study.
For the group of patients with other NCFCS, we used interim data from the same multicenter genotype-phenotype correlation study, which is still ongoing.13,15 For patients with NS, Van der Burgt's diagnostic criteria were used10; in those with cardiofaciocutaneous syndrome we used the cardiofaciocutaneous index,16 and where Costello syndrome was suspected, the diagnosis was considered confirmed if the HRAS mutation was identified.17 Clinical data for all of these patients were collected using the same methodology described for patients with LS.
Mutation TestingBlood samples were obtained from patients and their families after they had provided informed consent. Genomic DNA was extracted using standard procedures. Polymerase chain reaction amplification was performed using the primers and cycling parameters originally described by Tartaglia et al.18 This was followed by bidirectional sequencing of the coding regions and adjacent intronic regions using an ABI Prism Genotyper®. The SeqScape 2.5 software was used to analyze the electrophoretograms obtained.
Statistical AnalysisStatistical analysis was performed using Fisher exact test. Statistical significance was set at P<.05. The analysis was performed using SPSS 19.0.
RESULTSThe study included 19 patients (13 men, 6 women; age at diagnosis, 11 months to 49 years; mean age, 7.4 years). Cases were referred from 9 hospitals in 5 Spanish regions and 1 hospital in Belgrade (Serbia). Five patients were identified as familial cases (families A and B; 26% of cases; 95% confidence interval [95%CI], 9.1%-51.2%), and the rest were considered sporadic. Table 1 summarizes the phenotypic and molecular findings. Of the total, 15 met Voron's clinical criteria and 4 were considered to have a “partial form of LS”. The latter had clinical features typical of LS but did not have multiple lentigine syndrome or a family history of LS. All four were carriers of the p.Thr468Met mutation in PTPN11, which is typical of LS, and were of pediatric age at the time of the evaluation. The cutaneous features of the syndrome may therefore appear over time as the patients develop. Craniofacial (100% when typical and suggestive phenotypes were included; 95%CI, 82.4%-100%) and cardiac (88%; 95%CI, 63.6%-98.5%) anomalies, and skin lesions (84%; 95%CI, 60.4%-96.6%) were the most frequently reported characteristics, followed by short stature (37%; 95%CI, 16.3%-61.6%) and genital abnormalities (cryptorchidism in 3 patients, representing 16% of the total and 23% of men, 95%CI, 5%-53.8%). Three patients were diagnosed with hearing loss, but a sensorineural component was only observed in 1 individual (5%; 95%CI, 0.1%-26%); 7 patients had psychomotor retardation (37%; 95%CI, 16.3%-61.6%), although it was only mild in all cases. The 15 patients with multiple lentigines had a complete phenotype (79%; 95%CI, 54.4%-93.9%) and 11 of them also had café-au-lait spots (58%; 95%CI, 33.5%-79.7%). One patient with a partial phenotype also had coffee stains, while the other 3, aged between 10 months and 14 years, had no skin lesions. Two unrelated patients (patient numbers 1 and 8, with mutations p.Thr468Met and p.Gln510Arg, respectively) showed no skin manifestations at the initial assessment but developed the characteristic multiple lentigines during follow-up, which highlights the condition's evolving nature.
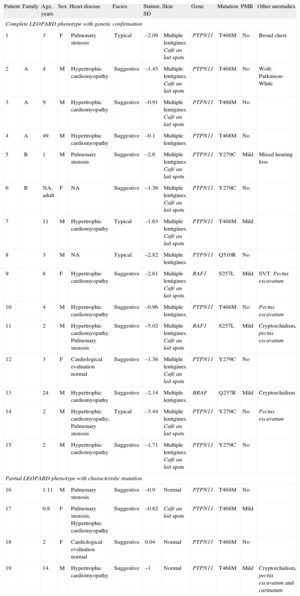
Clinical and Molecular Characteristics of 19 Patients With LEOPARD Syndrome
| Patient | Family | Age, years | Sex | Heart disease | Facies | Stature, SD | Skin | Gene | Mutation | PMR | Other anomalies |
| Complete LEOPARD phenotype with genetic confirmation | |||||||||||
| 1 | 3 | F | Pulmonary stenosis | Typical | –2.09 | Multiple lentigines. Café au lait spots | PTPN11 | T468M | No | Broad chest | |
| 2 | A | 4 | M | Hypertrophic cardiomyopathy | Suggestive | –1.45 | Multiple lentigines. Café au lait spots | PTPN11 | T468M | No | Wolf-Parkinson-White |
| 3 | A | 9 | M | Hypertrophic cardiomyopathy | Suggestive | –0.91 | Multiple lentigines. Café au lait spots | PTPN11 | T468M | No | |
| 4 | A | 49 | M | Hypertrophic cardiomyopathy | Suggestive | –0.1 | Multiple lentigines. | PTPN11 | T468M | No | |
| 5 | B | 1 | M | Pulmonary stenosis | Suggestive | –2.6 | Multiple lentigines. Café au lait spots | PTPN11 | Y279C | Mild | Mixed hearing loss |
| 6 | B | NA, adult | F | NA | Suggestive | –1.36 | Multiple lentigines. Café au lait spots | PTPN11 | Y279C | No | |
| 7 | 11 | M | Hypertrophic cardiomyopathy | Typical | –1.63 | Multiple lentigines. Café au lait spots | PTPN11 | T468M | Mild | ||
| 8 | 3 | M | NA | Typical | –2.82 | Multiple lentigines. | PTPN11 | Q510R | No | ||
| 9 | 8 | F | Hypertrophic cardiomyopathy | Suggestive | –2.61 | Multiple lentigines. Café au lait spots | RAF1 | S257L | Mild | SVT. Pectus excavatum | |
| 10 | 4 | M | Hypertrophic cardiomyopathy | Suggestive | –0.96 | Multiple lentigines. | PTPN11 | T468M | No | Pectus excavatum | |
| 11 | 2 | M | Hypertrophic cardiomyopathy. Pulmonary stenosis | Suggestive | –5.02 | Multiple lentigines. Café au lait spots | RAF1 | S257L | Mild | Cryptorchidism, pectus excavatum | |
| 12 | 3 | F | Cardiological evaluation normal | Suggestive | –1.36 | Multiple lentigines. Café au lait spots | PTPN11 | Y279C | No | ||
| 13 | 24 | M | Hypertrophic cardiomyopathy | Suggestive | –2.14 | Multiple lentigines. | BRAF | Q257R | Mild | Cryptorchidism | |
| 14 | 2 | M | Hypertrophic cardiomyopathy, Pulmonary stenosis | Typical | –3.44 | Multiple lentigines. Café au lait spots | PTPN11 | Y279C | No | Pectus excavatum | |
| 15 | 2 | M | Hypertrophic cardiomyopathy | Suggestive | –1.71 | Multiple lentigines. Café au lait spots | PTPN11 | Y279C | No | ||
| Partial LEOPARD phenotype with characteristic mutation | |||||||||||
| 16 | 1.11 | M | Pulmonary stenosis | Suggestive | –0.9 | Normal | PTPN11 | T468M | No | ||
| 17 | 0.8 | F | Pulmonary stenosis, Hypertrophic cardiomyopathy | Suggestive | –0.82 | Café au lait spots | PTPN11 | T468M | Mild | ||
| 18 | 2 | F | Cardiological evaluation normal | Suggestive | 0.04 | Normal | PTPN11 | T468M | No | ||
| 19 | 14 | M | Hypertrophic cardiomyopathy | Suggestive | –1 | Normal | PTPN11 | T468M | Mild | Cryptorchidism, pectus excavatum and carinatum | |
F, female; M, male; NA, not available; PMR, psychomotor retardation; SD, standard deviation; SVT, supraventricular tachycardias.
Familial cases are marked with letters (A and B). Cases 2 and 5 are the index cases of families A and B, respectively.
The most frequent congenital heart disease was hypertrophic cardiomyopathy (71%; 95%CI, 44%-89.7%), followed by pulmonary valve stenosis (35%; 95%CI, 14.2%-61.7%). Three patients (18%; 95%CI, 3.8%-43.4%) had both disorders. The only other congenital heart disease observed was aortic coarctation in 1 patient who also had hypertrophic cardiomyopathy. Coarctation in this patient resolved without corrective surgery, which would challenge the diagnosis of hypertrophic cardiomyopathy, although cardiomyopathy persisted several years after coarctation resolved. Only 2 (12%; 95%CI, 1.5%-36.4%) of the patients tested had regular cardiac testing. One patient was diagnosed at 2 months of age with Wolf-Parkinson-White syndrome following an episode of supraventricular tachycardia. One other patient also suffered supraventricular tachycardias. No patient experienced sudden death or required defibrillator implantation.
Molecular analysis of the PTPN11, RAF1, and BRAF genes detected mutations in 19 patients. The most frequent mutation was p.Thr468Met (10 patients, 53%; 95%CI 28.9%-75.6%). The p.Tyr279Cys amino acid change was identified in 2 related patients (mother and son, family B) and 3 unrelated patients (26% of the total series; 95%CI, 9.2%-51.2%). The p.Ser257Leu variant in RAF1 was detected in 2 other unrelated patients. Patients with mutations in RAF1 showed hypertrophic cardiomyopathy and some of the smallest statures in the series. Finally, we detected a change in the BRAF gene sequence in 1 patient.
To compare patients with LS and patients with other NCFCS, we included 87 patients with NS (PTPN11 mutation, 68 patients, 78%; SOS1 mutation, n=15, 17%; RAF1 mutation, n=4, 5%), 5 with cardiofaciocutaneous syndrome with a BRAF mutation, and 1 patient with Costello syndrome due to a mutation in HRAS. These patients came from 31 hospitals in 11 Spanish regions, 1 hospital in Belgrade (Serbia), and 1 hospital in Buenos Aires (Argentina). Table 2 shows the clinical features of each of these patient groups, and as compared to the LS patients. LS is related to the presence of multiple lentigines and café au lait spots (P<.001). Similarly, there is evidence of a strong association between LS and hypertrophic cardiomyopathy and greater height (P<.05).
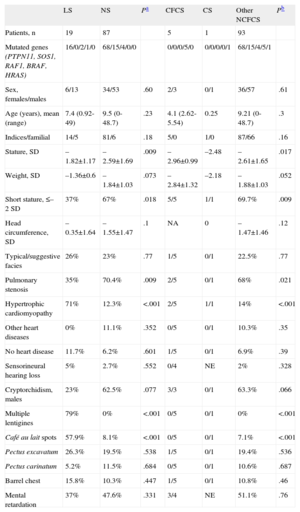
Comparison of Some Phenotypic Traits Among Patients With LEOPARD Syndrome and Patients With Other Neurocardiofaciocutaneous Syndromes
| LS | NS | Pa | CFCS | CS | Other NCFCS | Pb | |
| Patients, n | 19 | 87 | 5 | 1 | 93 | ||
| Mutated genes (PTPN11, SOS1, RAF1, BRAF, HRAS) | 16/0/2/1/0 | 68/15/4/0/0 | 0/0/0/5/0 | 0/0/0/0/1 | 68/15/4/5/1 | ||
| Sex, females/males | 6/13 | 34/53 | .60 | 2/3 | 0/1 | 36/57 | .61 |
| Age (years), mean (range) | 7.4 (0.92-49) | 9.5 (0-48.7) | .23 | 4.1 (2.62-5.54) | 0.25 | 9.21 (0-48.7) | .3 |
| Indices/familial | 14/5 | 81/6 | .18 | 5/0 | 1/0 | 87/66 | .16 |
| Stature, SD | –1.82±1.17 | –2.59±1.69 | .009 | –2.96±0.99 | –2.48 | –2.61±1.65 | .017 |
| Weight, SD | –1.36±0.6 | –1.84±1.03 | .073 | –2.84±1.32 | –2.18 | –1.88±1.03 | .052 |
| Short stature, ≤–2 SD | 37% | 67% | .018 | 5/5 | 1/1 | 69.7% | .009 |
| Head circumference, SD | –0.35±1.64 | –1.55±1.47 | .1 | NA | 0 | –1.47±1.46 | .12 |
| Typical/suggestive facies | 26% | 23% | .77 | 1/5 | 0/1 | 22.5% | .77 |
| Pulmonary stenosis | 35% | 70.4% | .009 | 2/5 | 0/1 | 68% | .021 |
| Hypertrophic cardiomyopathy | 71% | 12.3% | <.001 | 2/5 | 1/1 | 14% | <.001 |
| Other heart diseases | 0% | 11.1% | .352 | 0/5 | 0/1 | 10.3% | .35 |
| No heart disease | 11.7% | 6.2% | .601 | 1/5 | 0/1 | 6.9% | .39 |
| Sensorineural hearing loss | 5% | 2.7% | .552 | 0/4 | NE | 2% | .328 |
| Cryptorchidism, males | 23% | 62.5% | .077 | 3/3 | 0/1 | 63.3% | .066 |
| Multiple lentigines | 79% | 0% | <.001 | 0/5 | 0/1 | 0% | <.001 |
| Café au lait spots | 57.9% | 8.1% | <.001 | 0/5 | 0/1 | 7.1% | <.001 |
| Pectus excavatum | 26.3% | 19.5% | .538 | 1/5 | 0/1 | 19.4% | .536 |
| Pectus carinatum | 5.2% | 11.5% | .684 | 0/5 | 0/1 | 10.6% | .687 |
| Barrel chest | 15.8% | 10.3% | .447 | 1/5 | 0/1 | 10.8% | .46 |
| Mental retardation | 37% | 47.6% | .331 | 3/4 | NE | 51.1% | .76 |
CFCS, cardiofaciocutaneous syndrome; CS, Costello syndrome; LS, LEOPARD syndrome; NA, not available; NCFCS, neurocardiofaciocutaneous syndromes; NE, not evaluable; NS, Noonan syndrome; SD, standard deviations.
LS: 15 patients with full LEOPARD phenotype and 4 patients with partial LEOPARD phenotype and T468 M mutation in PTPN11 (data expressed as a percentage).
NS: 87 patients with genetically confirmed NS.
CFCS: 5 patients with genetically confirmed CFCS (data expressed in ratios).
CS: 1 case of genetically confirmed CS (data expressed in ratios).
Other NCFCS: patients with NCFCS other than LEOPARD (NS+CFCS+CS; data expressed as a percentage).
As some authors have suggested, a classification of cardiomyopathies that takes into account their underlying molecular characteristics could contribute to more appropriate management.19 In the case of hypertrophic cardiomyopathy, the relevance of both NS and LS should be borne in mind.20 This is particularly true when, from a cardiological perspective, the accompanying phenotype can vary from fatal cases to completely asymptomatic patients. Only a high level of suspicion will allow the clinician to consider this diagnostic option when there is little evidence.
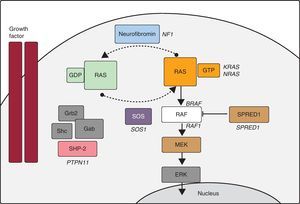
In recent years, advances in molecular biology have allowed us to elucidate many aspects of the etiology of NS and other entities with overlapping phenotypes (LS, Costello syndrome, cardiofaciocutaneous syndrome, neurofibromatosis type 1, and Legius syndrome). Some authors group these disorders under the name of NCFCS,21 RAS-MAPK syndromes, or rasopathies, as it appears that Ras/MAPK pathway dysregulation lies at the root of all of them (Figure). In NS, PTPN11 mutations have been identified in approximately 50% of patients, and mutations have been described in other genes of the RAS-MAPK pathway (SOS1,22RAF1,8KRAS,23MAP2K1,24BRAF,9NRAS,25 and SHOC226). Even today, there is no defined genetic cause in about 30% of patients diagnosed with NS.
Ras-MAPK cascade. The binding of a growth factor to a tyrosine kinase receptor activates intracellular effectors such as SHP2, which in turn recruit guanine nucleotide exchange factors such as SOS1 that promote GDP/GTP exchange in RAS proteins. The latter are activated by phosphorylation. Consequently, Ras-GTP activates the different RAF isoforms (RAF1, BRAF), MEK (MEK1, MEK2) and, finally, ERK.
In LS, about 85% of patients have mutations in PTPN11. Eleven mutations have been described in PTPN11 but, of those, 65% correspond to 2 highly recurrent mutations (p.Thr468Met7 and p.Tyr279Cys). In approximately one third of PTPN11 negative patients, mutations have been identified in RAF1,8 another gene in the RAS-MAPK cascade. Finally, mutations have been reported in BRAF,9,27 a gene whose mutations were primarily associated with cardiofaciocutaneous syndrome.
In recent decades, molecular studies have proven useful in providing differential diagnoses between these overlapping entities, as illustrated by several cases in our series. Among our patients, p.Thr468Met was the most common mutation in PTPN11, followed by p.Tyr279Cys. During evolutionary monitoring of patients with the p.Thr468Met mutation, the appearance of multiple lentigines led to a modification of the diagnosis in 2 cases. For that reason, and following previous authors,7 we considered pediatric patients with NS due to p.Thr468Met to be a partial phenotype of LS. Mutations with changes in amino-acid Gln510 have been associated with both NS and LS28; in our series, there were patients diagnosed with NS who showed sequence changes that predicted amino acid changes due to other residues (p.Gln510Glu, p.Gln510Pro). As these were adult patients, no change in diagnosis was expected and they were not included in the study. Patient 8, on the other hand, had the p.Gln510Arg variant and developed lentiginosis during pediatric clinical monitoring, a development which led to a modification of the diagnosis. In the case of RAF1, the p.Ser257Leu mutation was identified in 2 cases. In one patient who was negative for PTPN11 and RAF1, the BRAF mutation was identified, a finding which shows the relevance of studying this gene in patients with LS. Our study confirms the substantial benefits of carrying out genetic studies in patients with LS, and illustrates its close association with the PTPN11 gene and, to a lesser extent, RAF1 and BRAF.
The main diagnostic features of this syndrome are its cutaneous manifestations, which sometimes do not fully develop until after puberty29,30; deafness, which is not as common as in the initial descriptions of the syndrome; and congenital heart disease. Although pulmonary valve stenosis was initially described as the most common heart disease observed, hypertrophic cardiomyopathy is now more frequently identified.7,11,31 In our series, this congenital heart condition was more significantly associated with LS than were other NCFCS. In our setting, congenital heart disease has led to the definitive diagnosis in a large proportion of cases, and remains the most dangerous comorbidity in these patients.32 Pulmonary valve stenosis was identified in 6 of our 19 patients, making it the second most common cardiac diagnosis. Three patients had both conditions simultaneously. Both diagnoses should lead us to consider the possibility of a broader malformation. The 3-year-old patient in whom no congenital heart disease was found remains under observation in order to rule out the evolutionary occurrence of structural heart abnormalities, as described previously.33 Although in our series there were no fatal events and defibrillator use was not required in any of the patients, the oldest in the series was referred to a cardiac unit for further study because of syncope. In fact, it has been reported that LS patients with hypertrophic cardiomyopathy appear to be at increased risk of adverse events during follow-up.32 Among the cardiac disorders, although conduction defects are frequent, the Wolf-Parkinson-White syndrome described in one of our patients is not a common manifestation.
The phenotypic overlap between LS, NS, and neurofibromatosis type 1 makes it difficult to correctly classify these patients. Noonan syndrome-neurofibromatosis syndrome, which is related to mutations in the NF1 gene34 and characterized by the association between neurofibromatosis type 1 and NS manifestations, presents characteristics that are very similar to LS. The diagnosis of a congenital heart condition such as hypertrophic cardiomyopathy in patients with Noonan syndrome-neurofibromatosis makes it advisable to start with a genetic study of PTPN11 rather than with NF1.35 Multiple lentigines and café au lait spots are common in all 3 entities. Just as café au lait spots increase in number and size with age in these entities, multiple lentigines are rare in younger children. For this reason, some authors recommend evaluating for LS when diagnosing a patient younger than 1 year of age with NS associated with café au lait spots.29 Distinguishing between multiple lentigines and nevi may be particularly complex in some patients, and some authors propose including melanocytic lesions in the LS spectrum.36 In our series, the diagnosis was limited, whenever possible, to patients with lentiginous lesions. This is illustrated by a case described in Ezquieta et al.13 The patient suffered NS stemming from the p.Asn308Asp amino acid change in PTPN11 and had multiple hyperpigmented lesions, as did his mother, who had tested negative in the mutation study. These results indicated that the multiple nevus lesions observed in mother and child were due to a cause other than mutations in PTPN11. As indicated in earlier observations, we have demonstrated that LS is associated with a taller stature than other NCFCS.
CONCLUSIONSPulmonary valve stenosis and particularly hypertrophic cardiomyopathy are cardiological findings which may provide the key to identifying the syndrome. Given the potential clinical implications of hypertrophic cardiomyopathy, patients within the clinical spectrum of NS and particularly those with LS should be actively evaluated for this disease. The criteria originally described by Voron et al. in 1976 are still helpful in classifying these patients in terms of diagnosis. Nevertheless, the carriers of LS-associated anomalies that do not meet these criteria should be monitored over time because some skin manifestations, particularly multiple lentigines, may be delayed until late puberty.
FUNDINGFondo de Investigaciones Sanitarias (PI 06/1179).
CONFLICTS OF INTERESTNone declared.
The authors would like to thank the patients and their families for collaborating on the study as well as the clinicians who could not be included as authors. They include Drs. López-Siguero (Hospital Carlos Haya, Málaga), Barrio, and García-Sagredo (Hospital Ramón y Cajal, Madrid), Kuburovic (Mother and Child Healthcare Institute, Serbia), Gracia (Hospital Universitario La Paz, Madrid), Gener Querol (Hospital Universitario de Cruces, Barakaldo, Vizcaya), González-Meneses (Hospital Virgen del Rocío, Sevilla) and Aleixandre Blanquer (Hospital General Universitario de Elda, Alicante). Begoña Ezquieta is a researcher attached to U753 of the CIBER de Enfermedades Raras.