Keywords
INTRODUCTION
Bifascicular blocks (BFB) are a specific type of conduction system disorders. Its prevalence is 1% to 1.5% in the adult population according to data from the Framingham study.1 BFB patients have a higher probability of progression to advanced atrioventricular block (AVB) and increased risk of ventricular arrhythmias, which results in an increase in mortality when compared to the general population.2
Syncope in patients with BFB is often the result of advanced AVB or ventricular arrhythmias, and occurs between 10% to 15% at 3 years with an annual incidence of AVB ranging between 5% and 11% according to different series.3-5 In asymptomatic patients, this is lower, ranging from 0.6% to 0.8%.6 Syncopal recurrences can be suppressed successfully by the permanent implantation of a pacemaker (PM), although this therapy does not improve survival.2
In patients with BFB, the presence of syncope and documentation of prolonged HV intervals in electrophysiological studies (EPS) are independent predictors of advanced AVB.4,6 However, the sensitivity and specificity of the EPS has been questioned in some studies and there is now a difficult consensus on the limit value of the HV interval necessary to indicate the implementation of a pacemaker, ranging from 45 milliseconds (ms) in initial studies by Narula et al7 to 55 ms in studies by Dhingra et al3 and reaching 70 ms in the series by Scheinman et al.5 The currently accepted value is ≥70 ms in symptomatic patients and ≥100 ms in asymptomatic patients.8,9
For all these reasons, the aim of our study is to determine the interval cut-off point that best predicts the need to further assess whether PM and other clinical parameters may help in non-invasive risk stratification of BFB patients progressing to AVB during medium- to long-term follow-up.
METHODS
Patients
From March 1998 until December 2006, we prospectively studied 263 consecutive patients with BFB. The left bundle branch block (LBBB) and right bundle branch block (RBBB) were defined by standard criteria.10 The criteria for left anterior fascicular block (LAFB) and left posterior fascicular block (LPFB) were established as set forth in the literature.11 Inclusion criteria were the presence of BFB in ECG, for symptomatic patients (syncope or presyncope) as well as asymptomatic patients. Syncope was defined as sudden and complete loss of consciousness accompanied by loss of postural tone, with rapid and spontaneous reversion. Presyncope was defined as a situation of near-syncope, but without complete loss of consciousness.
Exclusion criteria were the presence of advanced heart failure with an indication of cardiac resynchronization therapy, a life expectancy of less than 1 year (mainly in patients with advanced malignancies), the observation of second or third grade transitional pre-EPS AVB and the associated presence of carotid sinus hypersensitivity. The study protocol was explained to each patient and signed authorization was obtained to conduct it.
Before the completion of the EPS, all patients underwent a complete medical history. An echocardiogram was also performed to rule out the presence of structural heart disease and assess the ejection fraction (EF) by Simpson's formula. Renal function was calculated by estimating the renal glomerular filtration rate (GFRe) with the MDRD formula (Modification on Diet on Renal Disease).12,13
We analyzed the following clinical variables: arterial hypertension, dyslipidaemia, diabetes, and smoking, NYHA functional class for heart failure, presence of structural heart disease and/or EF <5% and GFRe <60 mL/min/1.73m2.
Electrophysiological Study
The study was performed with the patient conscious and after fasting for at least 8 hours, and after removing any antiarrhythmic medication for at least 5 half-lives. Two 6 French tetrapolar electrocatheters were placed (Bard inc. Boston USA), with a 5 mm interelectrode distance, by percutaneous puncture through the right femoral vein. The catheters were positioned in the high right atrium and the other in the His position. The study protocol included measurement of baseline intervals (AH and HV), anterograde and retrograde Wenckebach points, the sinus node retrieval times with cycles of 600, 500, and 430 ms, and the anterograde and retrograde effective refractory periods of the atrioventricular node. Standard programmed atrial and ventricular stimulation was performed for arrhythmia induction, following the research protocol.
The result of the EPS is considered positive when the existence of an HV is documented for more than 60 ms in symptomatic patients. Following the publication of guidelines for treatment of syncope in 2004,8 the cut-off was changed to 70 ms. HV documentation greater than 100 ms in asymptomatic patients was also considered as a positive EPS. In patients with no EPS diagnosis, tests with pharmacological stressors using infra-his stressordrugs (ajmaline 1 mg/kg to a maximum of 50 mg or Procainamide 10 mg/kg up to 1000 mg) were carried out. HV interval prolongation above 100 ms was considered a positive test. Intracavitary records were recorded and measured on a "lab duo system" polygraph (Bard Inc. Boston, USA) at a paper speed of 100 mm/s. Carotid sinus massage was performed on all patients to discard its hypersensitivity.
Treatment and Monitoring
All patients with positive EPS from HV prolongation had a PM implanted. For the patients who had a sustained ventricular tachycardia induced, an implantable cardioverter defibrillator (ICD) was implanted, following the guidelines by the European Society of Cardiology. All patients with devices were followed in the pacemaker unit at 1, 3, 6, and 12 months and then every 6-12 months. Symptomatic patients with negative EPS underwent tilt tests and/ or the implantation of an insertable Holter. In March 2007 a transversal telephone follow-up was carried out for all patients to know whether they had syncopal relapse, hospitalization and death from any cause.
All devices were programmed in VVI mode with a minimum frequency of 40 L/min. If documentation of significant AVB (AVB defined as third degree, AVB 2:1 or 2nd degree symptomatic AVB) were reprogrammed to the proper frequency. Patients with associated sinus node dysfunction were programmed at minimum frequencies of 60 L/min in DDD mode with AV intervals of 300 ms to promote intrinsic ventricular rhythm.
Verification through advanced AVB electrocardiographic recording or the demonstration of a ventricular pacing rate exceeding 10% were considered as needing PM. This point was chosen as the cut-off point, as lower figures may be due to vagal stimulation at night.
Statistical Analysis
Continuous variables are expressed in mean (standard deviation) (SD) and qualitative absolute frequency and percentage. Variables that did not fit the normal distribution are shown with median and percentiles 25 and 75 (P25-P75).The t test for independent samples was used to compare continuous variables and ANOVA or Mann-Whitney and Kruskal-Wallis test were used in case of non-normal distribution. Differences between percentages were compared using χ2 test and Fisher's correction when the number of expected values was <5.
The analysis of the need for a pacemaker was performed in a clinical model that included non-invasive clinical and electrocardiographic variables (clinical analysis) and separately in an electrophysiological model (electrophysiology analysis) through descriptive bivariate Cox analysis. Variables that were associated with a significance level P≤.1 in the bivariate Cox analysis in both models, were incorporated into the final model (joint analysis) and a multivariate Cox regression (backward stepwise) was conducted to confirm the independent predictive value of each parameter with a significant value of P<.05. The results are expressed with the hazard ratio (HR) and a 95% of CI. Finally, with these independent predictors, the likelihood of needing PM was identified for each variable separately and combining them.
To determine the cut-off value of HV that best predicts the need for PM, we examined the area under the receiver operating characteristic (ROC curve), the sensitivity and specificity in patients who completed at least 12 months of follow-up.
RESULTS
Clinical and Electrocardiographic Characteristics
Of the 263 patients initially included, 12 were discarded for associated carotid sinus hypersensitivity. Two other patients were excluded from the final analysis because they died before the first control of the PM. Therefore, 249 patients were analyzed (Table 1).
A total of 170 cases were evaluated for syncope, with a median of 3.8 [P25:1-P75:6] syncopes per patient. In 39 patients, the EPS was indicated by presyncopal signs and symptoms, and the other 40 were asymptomatic. Of these, 22 were referred for ablation of an arrhythmic substrate (12 atrial flutter, 10 nodal reentry tachycardia) and the remaining 18 for preoperative assessment of surgical risk.
Of the total of 170 patients, 116 (47%) had structural heart disease: ischaemia (44 patients), hypertension (44), idiopathic dilated cardiomyopathy (18), valvular (9), and hypertrophic obstructive cardiomyopathy (1). The median EF was 63% [P25:54%-P75:66%] and 24 (10%) was ≤35%.
The PR interval averaged 215(48) ms, without significant differences between the 3 types of BFB. The mean QRS interval duration was 144 (15) ms. Patients with LBBB had a wider QRS (152 [15] ms) than patients with RBBB LAFB + (138 [11] ms) or LPFB + RBBB (142 [11] ms), P<.001.
Electrophysiological Characteristics
The median of the AH was 116 [P25:98-P75:144] ms, and of the HV interval, 64 [P25:56-P75:74] ms. There was no difference in the HV interval between different types of BFB. Infra AV block was observed by atrial pacing in 7 (3%) patients. Pharmacological testing was performed with class I antiarrhythmic drugs in 99 patients (40%), which was positive (HV≥100ms) in 6 cases.
HV prolongation was correlated with increased QRS width (r=0.3; P=.01). Furthermore, it was found that the HV interval was higher in patients with structural heart disease (68, P25-P75:60-81 ms) compared to patients without heart disease (64, P25-P75:57-73 ms), P=.03. Patients with CF ≥II had a significantly higher HV interval (71, P25-P75:61-83 ms) than patients in FC I (64, P25-P75:57-73 ms), P=.01.
Programmed ventricular stimulation in 6 patients induced episodes of sustained monomorphic ventricular tachycardia, all with structural heart disease and depressed systolic function (ischaemic heart disease in 5 and dilated cardiomyopathy in 1). In patients without heart disease, no sustained ventricular tachycardia was induced.
Of the 249 patients included, the EPS was positive in 154 (62%) patients, most of them symptomatic (118 with syncope and 19 with presyncope), with a permanent ventricular pacing device being implemented in all of them (7 DAI and 147 PM).
Of all patients studied, in 132 the EPS was conducted before the publication of 2004 syncope guidelines so the HV cut-off for symptomatic patients was 60 ms. From 2004 until the end of the study, another 117 patients were studied.
Follow-up
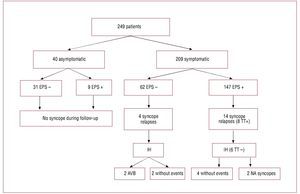
After a median follow up of 4.5 [2.16-6.41] years, the need for PM was determined in 102 (66%) of 154 patients with positive EPS. Of these, 45 patients were classified by percentage of stimulation ≥10% and in 57 from significant AVB documentation. Of the 102 patients, 77 had syncope, 16 presyncope, and 9 were asymptomatic. Figure 1 summarizes the evolution of patients with syncope during follow-up depending on the initial clinical results and the EPS.
Figure 1. Evolution of patients' symptoms and results of the electrophysiological study. EPS indicates electrophysiological study; IH, insertable Holter; NA, non-arrhythmic; TT, tilting test.
Sensitivity and Specificity of the HV Interval
To determine the cut-off value of HV interval that best predicts the need for PM, we selected 227 patients who were monitored for more than 1 year. For these patients, the cut-off of 70 ms recommended by the guidelines of the European Society of Cardiology, showed a sensitivity of 74% and a specificity of 78%. For these same patients, a cut-off of HV>64 ms presented a sensitivity increase to 83% and specificity decreased to 70% with a positive predictive value (PPV) of 54% and negative predictive value (NPV) of 91%, with an area under the ROC curve of 0.856 (95% CI, 0.81-0.91).This same cut-off point gets the best ratio of sensitivity/specificity if only considering patients with syncope or presyncope (sensitivity/ specificity, PPV, NPV of 83%/70%, 55% and 90%, respectively), with an area under the ROC curve of 0.844 (95% CI, 0.79-0.90).
HV stress analysis under the effect of antiarrhythmic drugs at a cut-off of 100 ms, showed an area under the ROC curve of 0.836 (95% CI, 0.69-0.98), a sensitivity of 40% and a specificity of 94%.
Prediction of Need for Pacemaker
Clinical Analysis
Clinical variables that were associated with an increased risk of needing a PM in the bivariate analysis and multivariate Cox analysis were syncopal or presyncopal symptoms, the PR interval >200 ms and a QRS width >140 ms (Tables 1 and 2).
Electrophysiological Analysis
The electrophysiological variables that increased the risk for the need for PM were an HV interval >64 ms and HV prolongation >100 ms with infra-his stressor drugs. The existence of retrograde conduction was shown to be a protective factor (Table 3). In multivariate analysis using only the Cox regression, the HV interval >64 ms was seen as a risk factor with an HR of 7.17 (4.44-11.60; P<.001).
Joint Analysis (Clinical and Electrophysiological)
The Cox multiple regression of variables that increased the risk of needing PM included the presence of syncopal or presyncopal symptoms, kidney failure, a QRS > 140ms and an HV interval > 64 ms (Table 4).
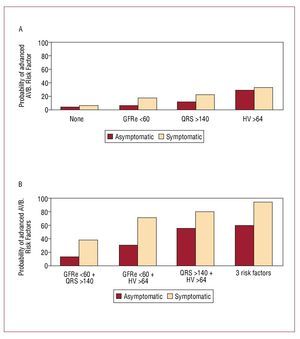
With these 4 variables, the annual probability of presenting an AV block was obtained depending on the number of variables present (Figure 2). It must be emphasized that the most important predictor was the HV interval, although this is only able to predict the need for PM in symptomatic patients in 33%. However, if you associate a QRS width > 140 ms, and renal failure, the probability increases to 95% in symptomatic patients and 59% of asymptomatic patients.
Figure 2. Graphs showing the annual probability of requiring a pacemaker in symptomatic and asymptomatic patients in terms of the associated risk factors (2A) and in relation to the various risk factors in symptomatic and asymptomatic patients (2B). AV block indicates atrioventricular block.
DISCUSSION
This study is the longest series and presents the longest period of follow-up of patients with BFB, mostly symptomatic, in our country. Our analysis confirms that the presence of symptoms and the width of baseline HV interval during the EPS are the most important predictors of risk of needing a PM in these patients. Furthermore, a QRS width above 140 ms and the presence of renal dysfunction (GFRe<60 mL/min/1.73m2) are also variables that predict the need of permanent ventricular pacing in patients with BFB and, therefore, reinforce the indication of definitive PM. It should be noted that in our analysis, the cut-off baseline HV interval that we recommend of > 64 ms is more sensitive but less specific than that recommended by the guidelines (70 ms).8,9 In other words, more PM than really necessary may be implanted with this cutoff point, but fewer patients who need stimulation would be left without it reducing the associated risk of syncopal relapse and the morbidity and mortality, especially in the elderly population.
It is noteworthy that over a third (35%) of patients with positive EPS and BFB apparently have no need for PM during follow-up. However, the fact that they remained asymptomatic suggests that stimulation rates below 10% may be sufficient to prevent syncope in patients with probable paroxysmal AVB.
In line with previous series, the presence of syncope/ presyncope is the main symptom that predicts the need for PM in patients with BFB.4,6 However, it has been proved that the prolonged HV interval (>64 ms) is the strongest predictor of need for PM (HR=6.6); therefore, we believe that EPS still has an important use in patients with syncope and BFB.5,14
Our study confirms that in patients with BFB of any type, there is a significant correlation between the duration of the HV interval and QRS interval duration, with an r=0.3 (P=.01).This had been demonstrated previously only in patients with LBBB or in relation to the stimulated QRS width.15,16 It must be emphasized that this correlation arises from longer cut-off points of the HV interval (>65 ms), since previous installments with lower cut-off points failed to correlate the QRS width with the HV interval.3,17
Renal dysfunction is an important factor in the need for PM. In the population studied in the presence of BFB and renal insufficiency with HV>64 ms without symptoms, the likelihood of needing PM is below 30% but rises to 71% if associated with syncope or presyncope (Figure 2). It is known that the greater degree of renal dysfunction, the higher the percentage of patients with wide QRS, BFB (especially LBBB) and advanced AVB.18,19 However, until now there was no data in the literature that related renal dysfunction with progression to sygnificant AVB, except in the presence of associated dyselectrolytaemia.20
In connection with the other electrophysiological parameters, infra-hisian blocking during atrial pacing, HV interval prolongation above 100 ms under the influence of drugs and infra-his stressors and presence of intra-hisian block, these have a high negative predictive value but an excessively positive predictive value. It should be emphasized that the cut-off of 100 ms with infra-his stressor drugs in our analysis shows a good specificity but low sensitivity (94% and 40%, respectively) in predicting need for PM, in relation to other series in the literature.21,22 However, analysing this data was not the initial objective of our study. In fact the test was performed only in 40% of patients (intermediate risk), which allows for only partial conclusions.
Limitations of the Study
To include patients with 10% over-stimulation 10% in the variable need for PM could overestimate the number of patients that actually evolved to significant AVB. However, we believe that patients who require pacing at a rate above 10%, when the PM is programmed in mode VVI at 40 L/min, probably have paroxysmal AVB and not only nocturnal hypervagotonia stimulation. Furthermore, the disappearance of symptoms in these patients supports this hypothesis.
Our series describes patients as symptomatic with presyncopal symptoms and BFB, and the previous series include only patients with syncope. However, in our analysis, patients with evident presyncopal symptoms ("near-syncope") were included, who also represented only 16% of the study population (39 patients). In this subgroup of patients the incidence of need for a PM was also significantly lower in patients with syncope (41% vs 45%).We therefore consider that the inclusion of patients with presyncope clearly does not influence the results obtained in this study.
In the evolution to significant AVB, the fact that these patients might have taken antiarrhythmic drugs for prevention of atrial fibrillation, for example, may have favoured the presence of significant AVB during monitoring. However, the proportion of patients in our series that have developed significant AVB is relatively low (<50% at 4.5 years of follow-up). This suggests that, rather than the influence of drugs, it must have been the natural evolution and degeneration of the conduction system that influenced the onset of significant AVB. On the other hand, it is difficult to understand how patients with negative EPS despite stressor infra-his drugs could respond to other antiarrhythmic drugs with less effect on the distal conduction system.
In the end, the behaviour of asymptomatic patients in our series may not be representative of the general behavior of the asymptomatic patients because there were few patients.
CONCLUSIONS
BFB patients present a higher risk of progression to significant AVB in the presence of evident syncopal or presyncopal symptoms, a baseline HV interval >64 ms, renal dysfunction GFRe <60 mL/min/1.73m2 and/or a QRS width >140 ms. HV interval prolongation above 100 ms under stressful effects of infra-his drugs and documentation of infra-hisian blocking during atrial pacing or intra-hisian blocking are additional predictive variables.
ABBREVIATIONS
AVB: atrioventricular block
BFB: bifascicular block
LAFB: left anterior fascicular block
LBBB: left bundle branch block
LPFB: left posterior fascicular block
RBBB: right bundle branch block
See editorial on pages 385-6
Correspondence: Dr. J. Martí-Almor.
Pg. Marítim, 25-29. 08003 Barcelona. España.
E-mail: jmarti@imas.imim.es
Received February 12, 2009.
Accepted for publication October 19, 2009.